knitr::include_graphics("assets/win11/documents.png")
In times of cloud save, tablets and app stores, dealing with files and directory paths gets less and less common in the day to day use with a PC. However, once you deal with external files in you R script (e.g. loading a .csv file), saving outputs or reports, you have to deal with directory and file structure. For beginners, this is often harder than the actual R code itself. So let’s quickly go over some basics of a file system on Windows and Linux respectively.
knitr::include_graphics("assets/win11/documents.png")
On a Windows operating system, usually, every user has their own “space” in which downloads, documents, images etc. are stored (?@fig-documents). When you now open a directory (e.g. the Rcourse directory Figure 2), you actually navigate through your file system - although Microsoft does a really good to hide the file path from you. If you click in the top bar, you can get the path. Note that in example Figure 2 the system language is German, but the actual path is in English. And further, Windows file paths use the backslash \ instead of the forward slash / to delineate directories. So, if you copy this path and want to use it in the R script, you have to change the backslashes to forward slashes.
knitr::include_graphics("assets/win11/kursordner.png")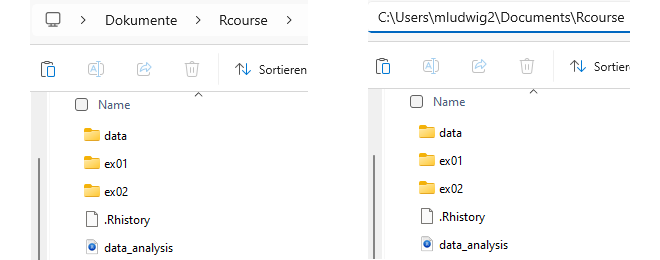
Regardless of you operating system, every file system has a root - a starting point from which all paths come from. On a unix like system (Linux and Mac) this is simply noted by a /, so a path like /home/marvin/rcourse starts with the root and navigates to sub-directories. On Windows, absolute file paths start with the letter of the hard drive, e.g. C:/. You can find out which letter you have in the This PC Window (Figure 3).
knitr::include_graphics("assets/win11/laufwerk_c.png")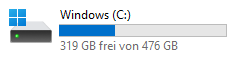
File paths that start with the root are called absolute. In R code, they are simply written as strings.
## Linux
"/home/marvin/projects/rcourse/session02/data/file.csv"## Windows
"C:\Users\Marvin\Dokumente\rcourse\session02\data\file.csv"Relative file paths do not start with the root of the file system, but with a so called working directory.
The working directory in R is a valuable feature that can saves a lot of nerves and time to navigate to files on your computer. You can check your current working directory with the getwd() function. In RStudio, you can also see your working directory as a path above the R console next to your R version number. The file browser of Rstudio also starts in your working directory by default. Use setwd() in order to change the working directory to some location (i.e. folder) on you computer. R and Rstudio know about the files in your working directory. You can think of it as the starting point of file paths.
getwd()
setwd("path/to/directory")To keep everything easy and consistent within R (at least for this course), I recommend setting a working directory either manually or with a Rstudio project and relative file paths to data.
setwd("/home/marvin/projects/rcourse/session02")
# If the R project is set up in the "session02" directory we can use relative paths:
# relative path to project root
data = read.csv("data/file.csv")Use the TAB Key in RStudio for navigation and auto-completion of file paths.
If you want to use RStudio Projects, there is a good blog entry in r-bloggers.com.